2 kinds of targeted therapies for the treatment of braf-positive non-small cell lung cancer
About Non Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC)
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively (adjuvant chemotherapy).
2 kinds of targeted drugs for the treatment of About braf-positive non-small cell lung cancer can be made in Laos
- Dabrafenib
- Trametinib
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells. Targeted therapies usually cause less harm to normal cells than chemotherapy or radiation therapy do. Monoclonal antibodies, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors are three types of targeted therapy being used to treat advanced, metastatic, or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer.
BRAF Inhibitors:
A gene that makes a protein that is involved in sending signals in cells and in cell growth. Mutated (changed) forms of the BRAF gene and protein have been found in many types of cancer. These changes can increase the growth and spread of cancer cells.
1, Dabrafenib
A drug used alone or with trametinib to treat certain types of anaplastic thyroid cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, and other solid tumors that have a certain mutation (change) in the BRAF gene. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Dabrafenib mesylate blocks certain proteins made by the mutated BRAF gene, which may help keep cancer cells from growing.
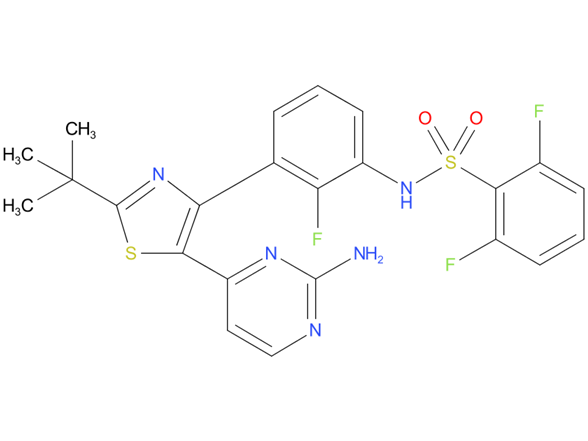
| Drug Profile | Dabrafenib is an inhibitor of some mutated forms of BRAF kinases with in vitro IC50 values of 0.65, 0.5, and 1.84 nM for BRAF V600E, BRAF V600K, and BRAF V600D enzymes, respectively. Dabrafenib also inhibits wild-type BRAF and CRAF kinases with IC50 values of 3.2 and 5.0 nM, respectively, and other kinases such as SIK1, NEK11, and LIMK1 at higher concentrations. Some mutations in the BRAF gene, including those that result in BRAF V600E, can result in constitutively activated BRAF kinases that may stimulate tumor cell growth. Dabrafenib inhibits cell growth of various BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumors in vitro and in vivo. |
| Alternative Names | 2118436; DRB 436; GSK 2118436A; GSK-2118436; Taffiner; Tafinlar; Tafinra; Tafinrar |
| Originator | GlaxoSmithKline |
| Developer | BeiGene; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; GlaxoSmithKline; National Cancer Institute (USA); Novartis; University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Fluorobenzenes; Pyrimidines; Small molecules; Sulfonamides; Thiazoles |
| Mechanism of Action | Proto oncogene protein b raf inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Malignant melanoma; Thyroid cancer; Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are seven patents protecting this compound. Dabrafenib mesylate has one hundred and fifty-two patent family members in forty-five countries. |
2, Trametinib
A drug used alone or with dabrafenib to treat certain types of anaplastic thyroid cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, and other solid tumors that have a certain mutation (change) in the BRAF gene. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide blocks proteins called MEK1 and MEK2, which may help keep cancer cells from growing.
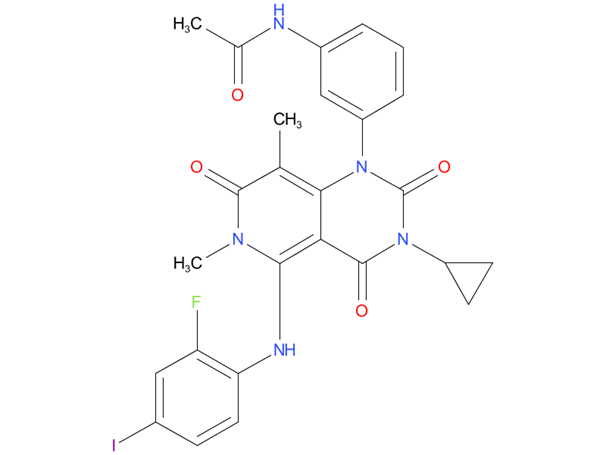
| Drug Profile | a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 activation and of MEK1 and MEK2 kinase activity. MEK proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation |
| Alternative Names | 1120212; CE-Trametinib; GSK-1120212; GSK-1120212B; JTP-74057; Mecinist; Mekinist; Mekinisuto; Tasu Mekinisuto; TMT-212; Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide; Trametinib DMSO |
| Originator | Japan Tobacco |
| Developer | BeiGene; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; GlaxoSmithKline; Japan Tobacco; M. D. Anderson Cancer Center; Merck Sharp & Dohme; National Cancer Institute (USA); Novartis; Pfizer; University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center |
| Class | 2 ring heterocyclic compounds; Amides; Antidementias; Antineoplastics; Cyclopropanes; Fluorobenzenes; Iodobenzenes; Pyridines; Pyrimidines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | MAP kinase kinase 1 inhibitors; MAP kinase kinase 2 inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Malignant melanoma; Thyroid cancer; Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are nine patents protecting this compound. Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide has one hundred and fifty-two patent family members in forty-five countries. |
Contact us to help you access the Lao pharmaceutical industry
RxLibra started its entrepreneurial journey with the vision of advancing the Lao pharmaceutical industry and becoming a global company. RxLibra is the first company in Laos to focus on exporting life-saving cancer drugs to Asia, Africa and Latin America.
Click & Contact us ?
The WTO’s Council for Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) :Under this license, the Lao pharmaceutical industry, as well as the pharmaceutical industry in similar countries(Bangladesh, Nepal, etc.), will be able to manufacture many drugs without patent authorization.
Reference:
《WTO members agree to extend drug patent exemption for poorest members》https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/news15_e/trip_06nov15_e.htm
《Product Patent Protection, the TRIPS LDC Exemption and the Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Industry》https://www.twn.my/title2/IPR/pdf/ipr17.pdf