7 targeted drugs for acute myeloid leukemia
About Acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are made.Acute myelogenous leukemia is also known as acute myeloid leukemia, acute myeloblastic leukemia, acute granulocytic leukemia and acute nonlymphocytic leukemia.
The main treatment for most types of AML is chemotherapy, sometimes along with a targeted therapy drug. This might be followed by a stem cell transplant. Other drugs (besides standard chemotherapy drugs) may be used to treat people with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Surgery and radiation therapy are not major treatments for AML, but they may be used in special circumstances.
7 Targeted Therapy Drugs for AML can be ordered in Laos
Targeted therapies are a kind of precision medicine. Targeted therapies for cancer work by acting on the proteins that control how cancer cells grow and divide. This is different from chemotherapy, which works by killing rapidly growing cells.
- Midostaurin
- Gilteritinib
- Quizartinib
- Ivosidenib
- Enasidenib
- Venetoclax
- Glasdegib
FLT3 inhibitors
Drugs that target the FLT3 mutation are called FLT3 inhibitors.
1、Midostaurin
Midostaurin may be used alongside chemotherapy in people newly diagnosed with AML with the FLT3 mutation. It is taken orally twice a day. How often a person needs to take midostaurin may vary depending on what phase of treatment they’re in.
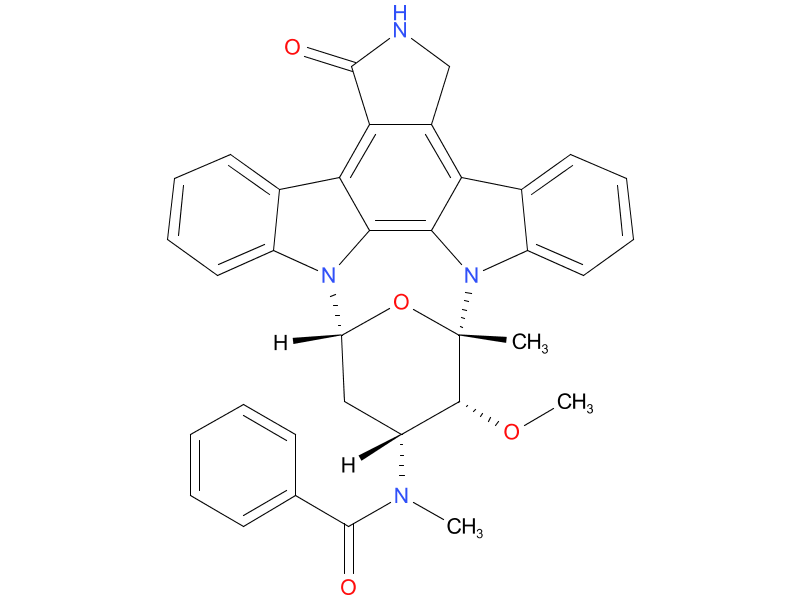
| Drug Profile | Midostaurin is a small molecule that inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases. In vitro biochemical or cellular assays have shown that midostaurin or its major human active metabolites CGP62221 and CGP52421 inhibit the activity of wild type FLT3, FLT3 mutant kinases (ITD and TKD), KIT (wild type and D816V mutant), PDGFR-alfa/beta, VEGFR2, as well as members of the serine/threonine kinase PKC (protein kinase C) family. Midostaurin demonstrated the ability to inhibit FLT3 receptor signaling and cell proliferation, and it induced apoptosis in leukemic cells expressing ITD and TKD mutant FLT3 receptors or overexpressing wild type FLT3 and PDGF receptors. Midostaurin also demonstrated the ability to inhibit KIT signaling, cell proliferation and histamine release and induce apoptosis in mast cells. |
| Alternative Names | 4-N-benzoyl staurosporine; Benzoylstaurosporine; CGP 41251; N-benzoyl-staurosporine; PKC412; PKC412A; Rydapt |
| Originator | Novartis |
| Developer | Massachusetts General Hospital; Mayo Clinic; National Cancer Institute (USA); Novartis; Novartis Oncology; Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Carbazoles; Eye disorder therapies; Indole alkaloids; Skin disorder therapies; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors; Platelet derived growth factor alpha receptor antagonists; Platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor antagonists; Protein kinase C inhibitors; Proto oncogene protein c-kit inhibitors; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Acute myeloid leukaemia; Systemic mastocytosis |
| Patent Information | Midostaurin has patent protection in the US, Europe and Japan covering its method of use with expiry in 2030, 2024 and 2024, respectively (Novartis annual report, 2017). A European and a Japanese patent on formulation is set to expire in 2020. |
2、Gilteritinib
Gilteritinib is also for people with the FLT3 mutation but is reserved for people whose cancer has come back or for whose cancer previous treatments did not work as hoped. It is taken orally once a day.
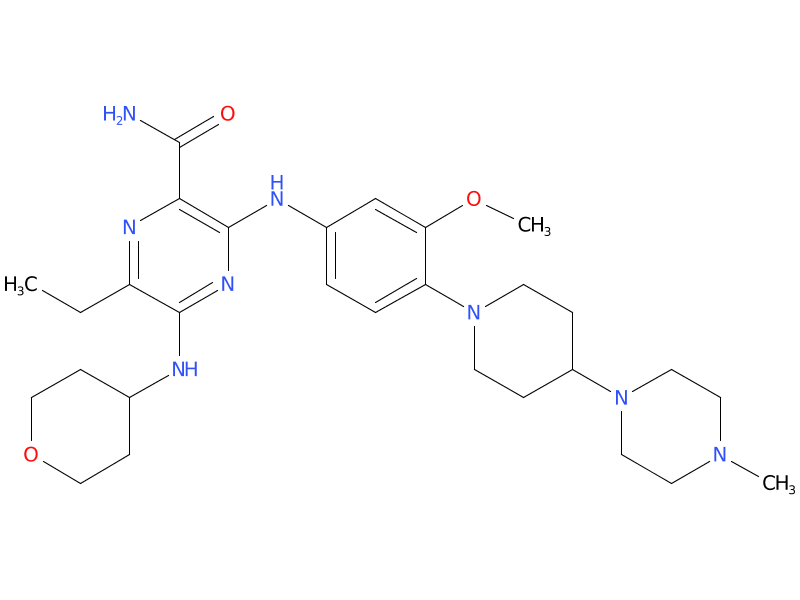
| Drug Profile | Gilteritinib is a small molecule that inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases, including FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3). Gilteritinib demonstrated the ability to inhibit FLT3 receptor signaling and proliferation in cells exogenously expressing FLT3 including FLT3-ITD, tyrosine kinase domain mutations (TKD) FLT3-D835Y and FLT3-ITD-D835Y, and it induced apoptosis in leukemic cells expressing FLT3-ITD. |
| Alternative Names | ASP-2215; ASP2215 hemifumarate; Gilteritinib fumarate; XOSPATA |
| Originator | Astellas Pharma; Kotobuki Pharmaceutical |
| Developer | AbbVie; Astellas Pharma; Genentech |
| Class | Amides; Aniline compounds; Antineoplastics; Piperazines; Piperidines; Pyrans; Pyrazines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors; Axl receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors; Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Acute myeloid leukaemia; |
| Patent Information | Gilteritinib has sixty-three patent family members in twenty-nine countries.Xospata will be eligible for patent challenges on November 28, 2022. |
3、Quizartinib
Quizartinib is a small molecule receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, originally from Ambit Biosciences and later acquired by Daiichi Sankyo, that is currently under development for the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia. Quizartinib is sold under the brand name Vanflyta in Japan.
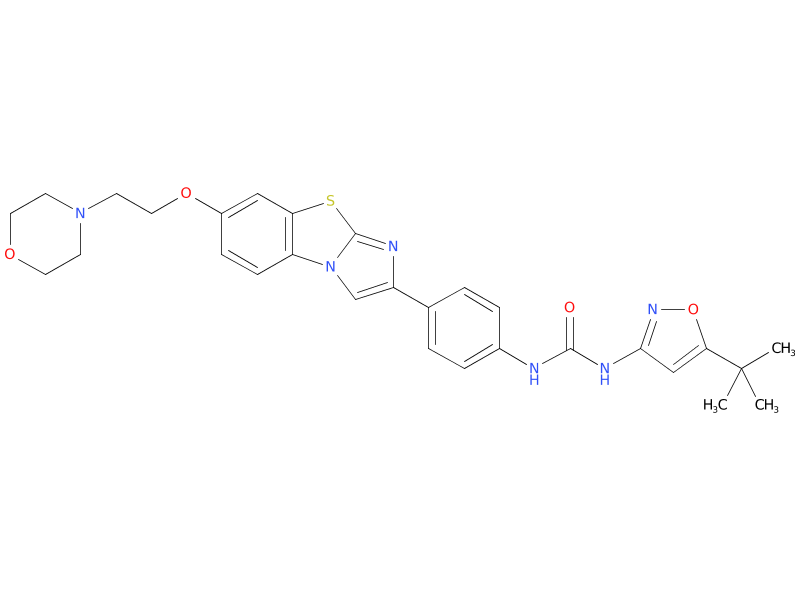
| Drug Profile | Quizartinib is the most selective type II FLT3 inhibitor and has shown the strongest single-agent activity in patient population with R/R-AML (acute myeloid leukemia) with FLT3 mutations. The FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitors act as direct inhibitors of FLT3 via competitive inhibition of ATP-binding sites in the FLT3 receptor. Type II FLT3 inhibitors bind the FLT3 receptor in the inactive conformation in a region adjacent to the ATP-binding domain. As a result of this binding affinity, these inhibitors prevent activity of ITD (the internal tandem duplication) mutations but do not target TKD (the tyrosine kinase domain) mutations |
| Alternative Names | AC-010220; AC-220; ASP-2689; VANFLYTA |
| Originator | Ambit Biosciences Corporation |
| Developer | Cancer Research UK; Cardiff University; Daiichi Sankyo Company; University Hospital Heidelberg; University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center |
| Class | 3-ring heterocyclic compounds; Antineoplastics; Benzothiazoles; Imidazoles; Isoxazoles; Morpholines; Phenylurea compounds; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors; Macrophage colony stimulating factor receptor antagonists; Platelet-derived growth factor receptor antagonists; Proto oncogene protein c-kit inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Acute myeloid leukaemia; |
| Patent Information | There are two hundred and eighty-six US patents protecting this investigational drug and two international patents.Most patents expire on March 27, 2035. |
IDH inhibitors
In some people with AML, the leukemia cells have a mutation in the IDH1 or IDH2 gene. These genes help the cells make certain proteins, which are also called IDH1 and IDH2. Mutations in one of these genes can stop blood cells from maturing the way they normally would.Targeted drugs called IDH inhibitors can block these IDH proteins. These drugs seem to work by helping the leukemia cells mature (differentiate) into more normal cells. Because of this, they are sometimes referred to as differentiation agents.
These drugs can be used to treat AML with an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation.
4、Ivosidenib
Ivosidenib is an IDH1 inhibitor. It can be used to treat AML with an IDH1 mutation, either as the first treatment in people who are older or are not healthy enough to tolerate strong chemo, or to treat AML that comes back after treatment or is no longer responding to other treatments.
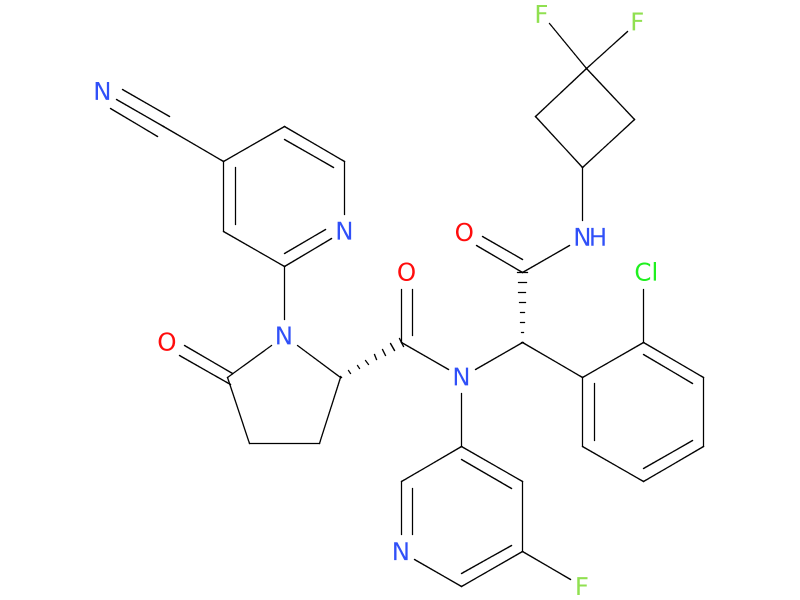
| Drug Profile | Ivosidenib is a small molecule inhibitor that targets the mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) enzyme. Susceptible IDH1 mutations are defined as those leading to increased levels of 2-hydroxyglutarate(2-HG) in the leukemia cells and where efficacy is predicted by 1) clinically meaningful remissions with the recommended dose of ivosidenib and/or 2) inhibition of mutant IDH1 enzymatic activity at concentrations of ivosidenib sustainable at the recommended dosage according to validated methods. The most common of such mutations are R132H and R132C substitutions. |
| Alternative Names | AG-120; CS 3010; S-95031; TIBSOVO |
| Originator | Agios Pharmaceuticals |
| Developer | Agios Pharmaceuticals; Bristol-Myers Squibb; CStone Pharmaceuticals; HOVON Foundation; University of Pittsburgh Medical Center |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Cyclobutanes; Nitriles; Pyridines; Pyrrolidines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Acute myeloid leukaemia; Cholangiocarcinoma; Glioma |
| Patent Information | This drug has one hundred and fourteen patent family members in thirty-seven countries.Tibsovo was eligible for patent challenges on July 20, 2022. |
5、Enasidenib
Enasidenib is an IDH2 inhibitor. It can be used to treat AML with an IDH2 mutation, either as the first treatment in people who are older or are not healthy enough to tolerate strong chemo, or to treat AML that comes back after treatment or is no longer responding to other treatments.
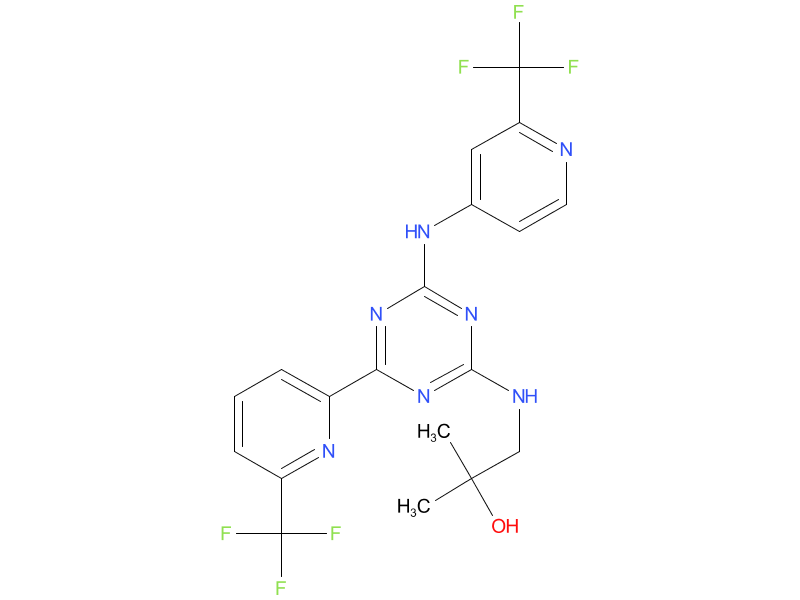
| Drug Profile | Enasidenib is a small molecule inhibitor of the isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) enzyme. Enasidenib targets the mutant IDH2 variants R140Q, R172S, and R172K at approximately 40-fold lower concentrations than the wild-type enzyme in vitro. Inhibition of the mutant IDH2 enzyme by enasidenib led to decreased 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) levels and induced myeloid differentiation in vitro and in vivo in mouse xenograft models of IDH2 mutated AML. In blood samples from patients with AML with mutated IDH2, enasidenib decreased 2-HG levels, reduced blast counts and increased percentages of mature myeloid cells. |
| Alternative Names | AG 221 mesylate; AG-221; AGI 12910 mesylate; AGI-12910; CC-90007; IDHIFA |
| Originator | Agios Pharmaceuticals |
| Developer | Agios Pharmaceuticals; Celgene Corporation; HOVON Foundation; Massachusetts General Hospital; University Health Network |
| Class | Amines; Antineoplastics; Fluorinated hydrocarbons; Propanols; Pyridines; Small molecules; Triazines |
| Mechanism of Action | Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Acute myeloid leukaemia; |
| Patent Information | This drug has one hundred and seven patent family members in thirty-nine countries.Idhifa was eligible for patent challenges on August 1, 2021. |
BCL-2 inhibitor
BCL-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) is one of a family of genes that regulates cell death, called apoptosis. The BCL-2 either inhibits or stops cell death (anti-apoptotic) or induces apoptosis (starting cell death). BCL-2 helps cell growth by blocking programmed cell death by promoting cell survival. Some types of lymphoma and particularly CLL are dependent on BCL-2 for their survival. The expression of this gene is strongly associated with resistance to chemotherapy.
All normal cells undergo programmed cell death. All cells live for a amount of time and then they die at a controlled rate. In some lymphomas, particularly CLL the BCL-2 gene allows them to survive. BCL-2 inhibitors are a targeted therapy that inhibits or stops this gene and that makes lymphoma cells die.
6、Venetoclax
Venetoclax targets BCL-2, a protein in cancer cells that helps them live longer than they should. This drug can be used with chemotherapy in people with newly diagnosed AML who are 75 years or older, or who are not healthy enough to tolerate strong chemo. It’s taken by mouth once a day.
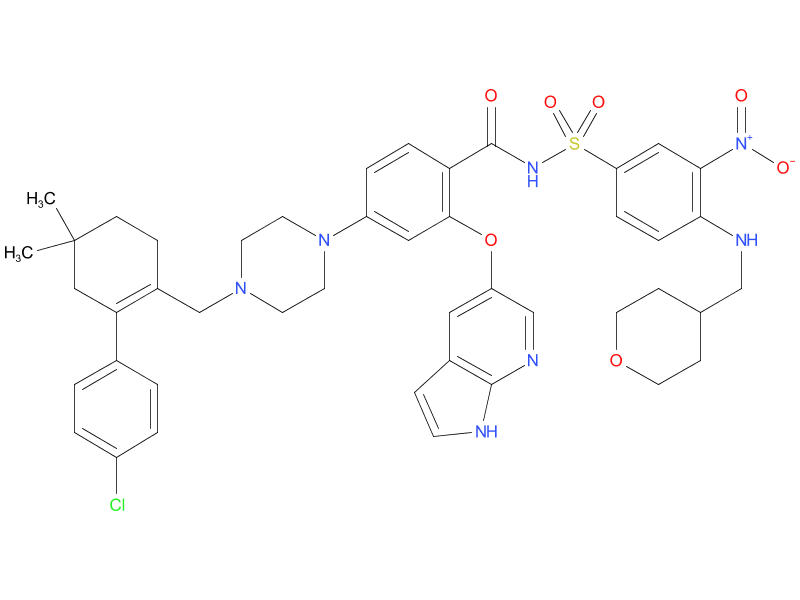
| Drug Profile | Venetoclax is a selective and orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of BCL-2, an anti-apoptotic protein. Overexpression of BCL-2 has been demonstrated in CLL cells where it mediates tumor cell survival and has been associated with resistance to chemotherapeutics. Venetoclax helps restore the process of apoptosis by binding directly to the BCL-2 protein, displacing pro-apoptotic proteins like BIM, triggering mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and the activation of caspases. In nonclinical studies, venetoclax has demonstrated cytotoxic activity in tumor cells that overexpress BCL-2. |
| Alternative Names | A-1195425.0; ABT 0199; ABT 199; GDC-0199; RG-7601; RO-5537382; Venclexta; VENCLYXTO; Venclyxto |
| Originator | Abbott Laboratories; Genentech; Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research |
| Developer | AbbVie; Celgene Corporation; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Emory University; Fondazione Italiana Linfomi; Gateway for Cancer Research; Genentech; Janssen Research & Development; M. D. Anderson Cancer Center; Nantes University Hospital; National Cancer Institute (USA); Nordic Lymphoma Group; Pharmacyclics; Roche; St. Jude Childrens Research Hospital; Syros Pharmaceuticals; University Health Network |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Benzamides; Heterocyclic bicyclo compounds; Piperazines; Pyrans; Pyridines; Pyrroles; Small molecules; Sulfonamides |
| Mechanism of Action | Apoptosis stimulants; Proto-oncogene protein c-bcl-2 inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; Acute myeloid leukaemia; Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; Multiple myeloma |
| Patent Information | This drug has one hundred and eighty-seven patent family members in forty-two countries.Venclexta was eligible for patent challenges on April 11, 2020. |
Hedgehog pathway inhibitor
AML cells can have mutations (changes) in genes that are part of a cell signaling pathway called hedgehog. The hedgehog pathway is crucial for the development of the embryo and fetus and is important in some adult cells, but it can be overactive in leukemia cells.
7、Glasdegib
Glasdegib is a drug that targets a protein in this pathway. It can be used with chemotherapy in people with newly diagnosed AML who are 75 years or older, or who are not healthy enough to tolerate strong chemo. In this group, it has been shown to help people live longer.
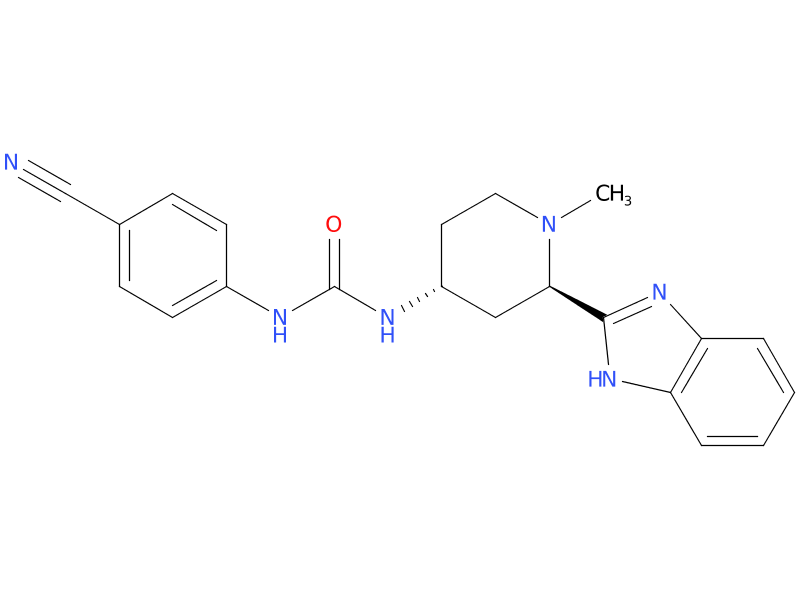
| Drug Profile | Glasdegib is an inhibitor of the Hedgehog pathway. Glasdegib binds to and inhibits Smoothened, a transmembrane protein involved in hedgehog signal transduction. |
| Alternative Names | 1095173-27-5; DAURISMO; PF 04; PF-04449913; PF-4449913 |
| Originator | Pfizer |
| Developer | Grupo Espanol de Trasplante Hematopoyetico y Terapia Celular; H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute; Pfizer; Yale University |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Benzimidazoles; Phenylurea compounds; Piperidines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Hedgehog cell-signalling pathway inhibitors; SMO protein inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Acute myeloid leukaemia; Myelodysplastic syndromes |
| Patent Information | This drug has eighty-five patent family members in forty-seven countries.Daurismo will be eligible for patent challenges on November 21, 2022. |
Contact us to help you access the Lao pharmaceutical industry
RxLibra started its entrepreneurial journey with the vision of advancing the Lao pharmaceutical industry and becoming a global company. RxLibra is the first company in Laos to focus on exporting life-saving cancer drugs to Asia, Africa and Latin America.
Click & Contact us ?
The WTO’s Council for Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) :Under this license, the Lao pharmaceutical industry, as well as the pharmaceutical industry in similar countries(Bangladesh, Nepal, etc.), will be able to manufacture many drugs without patent authorization.
Reference:
《WTO members agree to extend drug patent exemption for poorest members》https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/news15_e/trip_06nov15_e.htm
《Product Patent Protection,the TRIPS LDC Exemption and the Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Industry》https://www.twn.my/title2/IPR/pdf/ipr17.pdf