3 kinds of targeted therapies for the treatment of MET-mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer

About Non Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC)
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively (adjuvant chemotherapy).
3 kinds of targeted drugs for the treatment of About MET-mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer can be made in Laos
- Tepotinib
- Capmatinib
- Savolitinib
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells. Targeted therapies usually cause less harm to normal cells than chemotherapy or radiation therapy do. Monoclonal antibodies, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors are three types of targeted therapy being used to treat advanced, metastatic, or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer.
MET Inhibitors:
A gene that makes a protein that is involved in sending signals within cells and in cell growth and survival. Mutated (changed) forms of the MET gene may cause abnormal cells to grow and spread in the body. Mutations in the MET gene have been found in an inherited condition called hereditary papillary renal carcinoma (HPRC). Patients with HPRC have an increased risk of a type of kidney cancer called papillary renal carcinoma. MET gene mutations have also been found in liver cancer and head and neck cancer. The MET gene is a type of proto-oncogene and a type of receptor tyrosine kinase gene.
1, Tepotinib
A drug used to treat adults with non-small cell lung cancer that has spread to other parts of the body and has a certain mutation (change) in the MET gene. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Tepotinib hydrochloride blocks a protein made by the MET gene, which may help keep cancer cells from growing and spreading and may kill them.
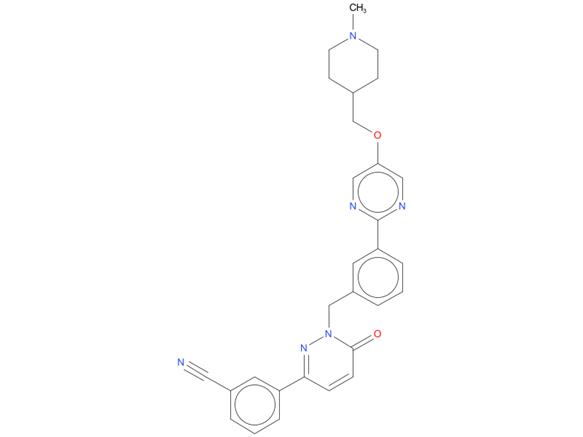
| Drug Profile | Tepotinib is a MET (mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor) tyrosine kinase inhibitor being developed for the treatment of solid tumours. It selectively binds to MET and inhibits MET phosphorylation disrupting the oncogenic MET receptor signalling caused by MET gene alterations, including both MET exon 14 (METex14) skipping alterations and MET protein overexpression. This results in cell death in tumour cells overexpressing MET protein or expressing constitutively activated MET protein. |
| Alternative Names | EMD-1214063; MSC-2156119; MSC-2156119J; TEPMETKO |
| Originator | EMD Serono; Merck KGaA |
| Developer | Null |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Nitriles; Piperidines; Pyridazines; Pyrimidines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Proto oncogene protein c met inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are eight patents protecting this compound. Tepotinib hydrochloride has seventy-four patent family members in thirty-three countries. |
2, Capmatinib
A drug used to treat adults with non-small cell lung cancer that has spread and has a certain mutation (change) in the MET gene. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Capmatinib hydrochloride blocks a protein made by the MET gene, which may help keep cancer cells from growing and may kill them.
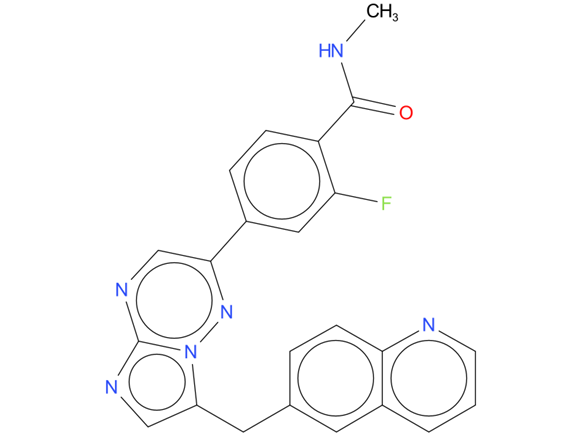
| Drug Profile | Capmatinib is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have a mutation that leads to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) exon 14 skipping as detected by an FDA-approved test. |
| Alternative Names | INC-280; INCB-028060; INCB-28060; TABRECTA; Tabrecta |
| Originator | Incyte Corporation |
| Developer | Array BioPharma; Novartis Oncology |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Benzamides; Fluorobenzenes; Heterocyclic bicyclo compounds; Imidazoles; Quinolines; Small molecules; Triazines |
| Mechanism of Action | Proto oncogene protein c met inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are five patents protecting this compound. Capmatinib hydrochloride has one hundred and sixty-two patent family members in forty-two countries. |
3, Savolitinib
Savolitinib is an experimental small molecule inhibitor of c-Met. It is being investigated for the treatment of cancer by AstraZeneca. It is in phase II clinical trials for adenocarcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma. It has been given conditional approval for these indication in China.
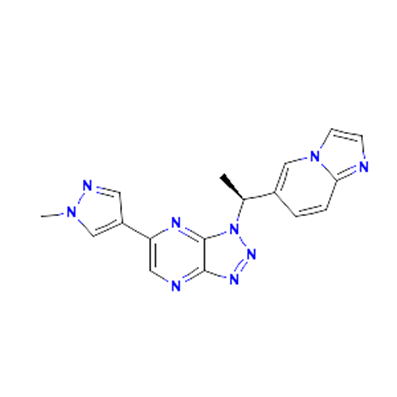
| Drug Profile | Savolitinib is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase with potential antineoplastic activity. Savolitinib selectively binds to and inhibits the activation of c-Met in an ATP-competitive manner, and disrupts c-Met signal transduction pathways. This may result in cell growth inhibition in tumors that overexpress the c-Met protein. C-Met encodes the hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and plays an important role in tumor cell proliferation, survival, invasion, and metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis; this protein is overexpressed or mutated in a variety of cancers. |
| Alternative Names | AZD-6094; HMP-504; HMPL-504; Orpathys; Volitinib; Voressa |
| Originator | Hutchison MediPharma |
| Developer | AstraZeneca; Hutchison MediPharma; HUTCHMED; National Cancer Institute (USA); Samsung Medical Center |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Imidazoles; Pyrazines; Pyrazoles; Pyridines; Small molecules; Triazoles |
| Mechanism of Action | Proto oncogene protein c met inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | NUll |
| Patent Information | Null |
Contact us to help you access the Lao pharmaceutical industry
RxLibra started its entrepreneurial journey with the vision of advancing the Lao pharmaceutical industry and becoming a global company. RxLibra is the first company in Laos to focus on exporting life-saving cancer drugs to Asia, Africa and Latin America.
Click & Contact us ?
The WTO’s Council for Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) :Under this license, the Lao pharmaceutical industry, as well as the pharmaceutical industry in similar countries(Bangladesh, Nepal, etc.), will be able to manufacture many drugs without patent authorization.
Reference:
《WTO members agree to extend drug patent exemption for poorest members》https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/news15_e/trip_06nov15_e.htm
《Product Patent Protection,the TRIPS LDC Exemption and the Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Industry》https://www.twn.my/title2/IPR/pdf/ipr17.pdf