7 kinds of targeted therapies for the treatment of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer
About Non small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC)
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively (adjuvant chemotherapy).
7 kinds of targeted drugs for the treatment of About EGFR- mutated non-small cell lung cancer can be made in Laos
- Erlotinib
- Gefitinib
- Afatinib
- Osimertinib
- Dacomitinib
- Mobocertinib
- Lazertinib
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells. Targeted therapies usually cause less harm to normal cells than chemotherapy or radiation therapy do. Monoclonal antibodies, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors are three types of targeted therapy being used to treat advanced, metastatic, or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer.
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors:
EGFRs are proteins found on the surface and inside certain cells, including cancer cells. Epidermal growth factor attaches to the EGFR inside the cell and sends signals to the tyrosine kinase area of the cell, which tells the cell to grow and divide. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors stop these signals and stop the cancer cell from growing and dividing. Erlotinib, gefitinib, afatinib, osimertinib, and dacomitinib are types of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Some of these drugs work better when there is also a mutation (change) in the EGFR gene.
1, Erlotinib
A drug used alone to treat certain types of non-small cell lung cancer and with gemcitabine hydrochloride to treat certain types of pancreatic cancer. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Erlotinib hydrochloride blocks a protein called EGFR, which may help keep cancer cells from growing. It is a type of tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Also called CP-358,774, OSI-774, and Tarceva.
| Drug Profile | A quinazoline derivative and ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENT that functions as a PROTEIN KINASE INHIBITOR for EGFR associated tyrosine kinase. It is used in the treatment of NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER. |
| Alternative Names | CP-358774; CP-358774-01; Erlotinib hydrochloride; NSC-718781; OSI-774; R-1415; RG-1415; RO-508231; Ro50-8231; Tarceva |
| Originator | OSI Pharmaceuticals |
| Developer | Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology; Astellas Pharma; Chugai Pharmaceutical; Eli Lilly and Company; European Thoracic Oncology Platform; Finnish Lung Cancer Group; Genentech; M. D. Anderson Cancer Center; Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center; National Cancer Institute (USA); Novartis; OSI Pharmaceuticals; Polyphenon Pharma; Roche; SCRI Development Innovations; Takeda Oncology; University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center; Wake Forest University School of Medicine |
| Class | Alkynes; Antineoplastics; Quinazolines; Skin disorder therapies; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Glioblastoma |
| Patent Information | There are twenty-three drug master file entries for erlotinib hydrochloride. Twelve suppliers are listed for this compound. |
2, Gefitinib
A drug used to treat non-small cell lung cancer that has spread to other parts of the body and has certain mutations (changes) in the EGFR gene. It is used in patients whose cancer has not already been treated with other anticancer therapy. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Gefitinib blocks certain proteins made by the EGFR gene, which may help keep cancer cells from growing. It may also prevent the growth of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow. Gefitinib is a type of tyrosine kinase inhibitor and a type of antiangiogenesis agent.
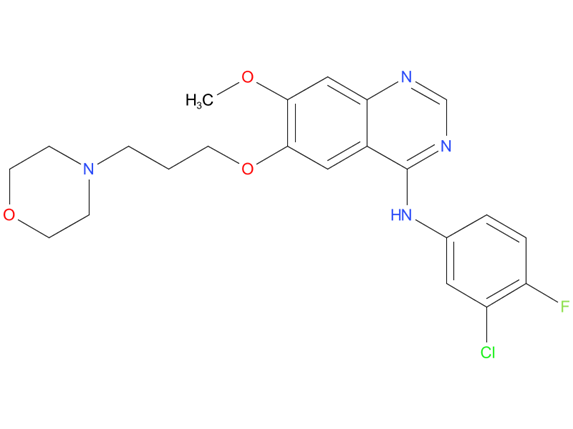
| Drug Profile | Gefitinib reversibly inhibits the kinase activity of wild-type and certain activating mutations of EGFR, preventing autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues associated with the receptor, thereby inhibiting further downstream signalling and blocking EGFR-dependent proliferation. |
| Alternative Names | Iressa; ZD-1839 |
| Originator | AstraZeneca |
| Developer | AstraZeneca; Brigham and Women’s Hospital; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Hutchison MediPharma; Massachusetts General Hospital; MedImmune; University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center |
| Class | Amines; Antineoplastics; Chlorobenzenes; Fluorobenzenes; Morpholines; Phenyl ethers; Quinazolines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are twelve drug master file entries for gefitinib. One supplier is listed for this compound. |
3, Afatinib
A drug used to treat certain types of non-small cell lung cancer that have spread to other parts of the body. It is used in patients whose cancer has not already been treated and has certain mutations (changes) in the EGFR gene or whose cancer got worse after treatment with platinum chemotherapy. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Afatinib dimaleate blocks certain proteins made by the EGFR gene, which may help keep cancer cells from growing. It may also prevent the growth of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow.
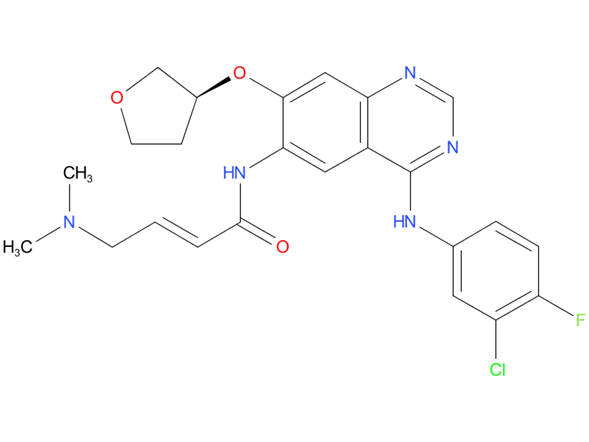
| Drug Profile | A quinazoline and butenamide derivative that acts as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptors (ERBB RECEPTORS) and is used in the treatment of metastatic NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER. |
| Alternative Names | Afatinib dimaleate; BIBW 2992 MA2; BIBW-2992; Gilotrif; Giotrif; Tomtovok; Tovok; Xovoltib |
| Originator | Boehringer Ingelheim |
| Developer | Null |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Quinazolines; Radiation-sensitising agents; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists; ERBB 2 receptor antagonists; ERBB 4 receptor antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Non-small cell lung cancer; CNS cancer; Pancreatic cancer |
| Patent Information | There are five patents protecting this compound and one Paragraph IV challenge. Afatinib dimaleate has one hundred and eighty-six patent family members in forty-six countries. |
4, Osimertinib
A drug used to treat adults with some types of non-small cell lung cancer that have certain mutations (changes) in the EGFR gene. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Osimertinib mesylate blocks certain proteins made by the mutated EGFR gene, which may help keep cancer cells from growing and may kill them.
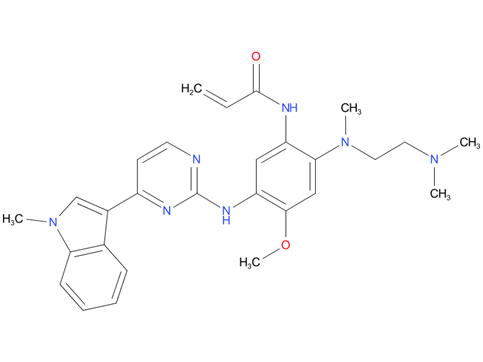
| Drug Profile | Osimertinib is a kinase inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which binds irreversibly to certain mutant forms of EGFR (T790M, L858R, and exon 19 deletion) at approximately 9-fold lower concentrations than wild-type. In cultured cells and animal tumor implantation models, osimertinib exhibited anti-tumor activity against NSCLC lines harboring EGFR-mutations (T790M/L858R, L858R, T790M/exon 19 deletion, and exon 19 deletion) and, to a lesser extent, wild-type EGFR amplifications. |
| Alternative Names | [11C]AZD9291; [11C]osimertinib; ADAURA; AZD-9291; Mereletinib; TAGRISSO; Tagrisso |
| Originator | AstraZeneca |
| Developer | AstraZeneca; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Eli Lilly and Company; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer; European Thoracic Oncology Platform; G1 Therapeutics; Genprex; HUTCHMED; Incyte Corporation; Kyushu University; Molecular Partners AG; National Cancer Institute (USA); National University Hospital (Singapore); Princess Margaret Hospital (University of Toronto); Singapore Clinical Research Institute; Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre; University of California at San Francisco |
| Class | Acrylamides; Amides; Aniline compounds; Antineoplastics; Dimethylamines; Indoles; Phenyl ethers; Pyrimidines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are three patents protecting this compound. Osimertinib mesylate has one hundred and sixty-eight patent family members in forty-two countries. |
5, Dacomitinib
A drug used to treat non-small cell lung cancer that has spread, has not already been treated, and has certain mutations (changes) in the EGFR gene. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Dacomitinib blocks certain proteins, which may help keep cancer cells from growing and may kill them. It is a type of tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Also called PF-00299804 and Vizimpro.
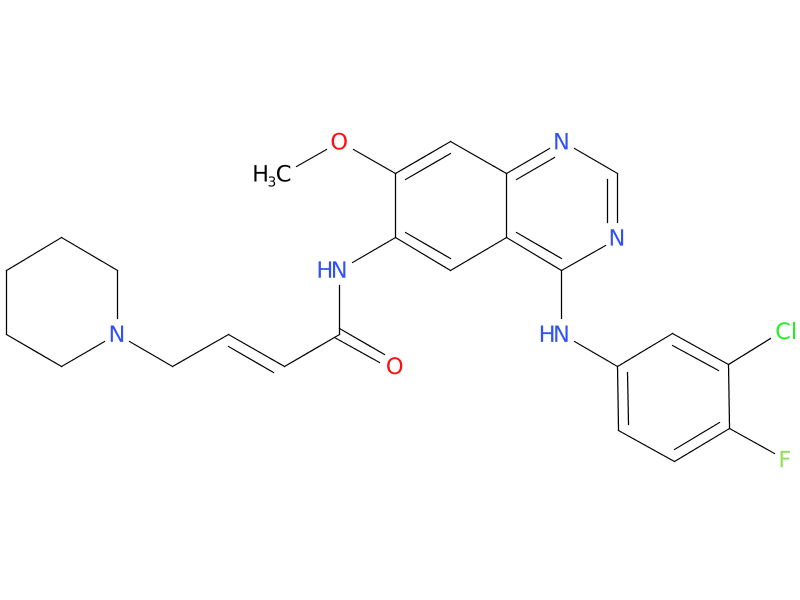
| Drug Profile | Dacomitinib is an irreversible inhibitor of the kinase activity of the human EGFR family (EGFR/HER1, HER2, and HER4) and certain EGFR activating mutations (exon 19 deletion or the exon 21 L858R substitution mutation). In vitro dacomitinib also inhibited the activity of DDR1, EPHA6, LCK, DDR2, and MNK1 at clinically relevant concentrations. |
| Alternative Names | Dacomitinib; PF-00299804; PF-299; PF-299804; PF-804; VIZIMPRO |
| Originator | Pfizer |
| Developer | Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori; Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center; Netherlands Cancer Institute; Pfizer; Seoul National University Hospital; SFJ Pharmaceuticals; University Health Network; University of California, San Diego |
| Class | Amides; Aniline compounds; Antineoplastics; Piperidines; Quinazolinones; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists; ERBB 2 receptor antagonists; ERBB 4 receptor antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are four patents protecting this compound. Dacomitinib has ninety-one patent family members in forty-seven countries. |
6, Mobocertinib
Mobocertinib is indicated for adults with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, whose disease has progressed on or after platinum-based chemotherapy.
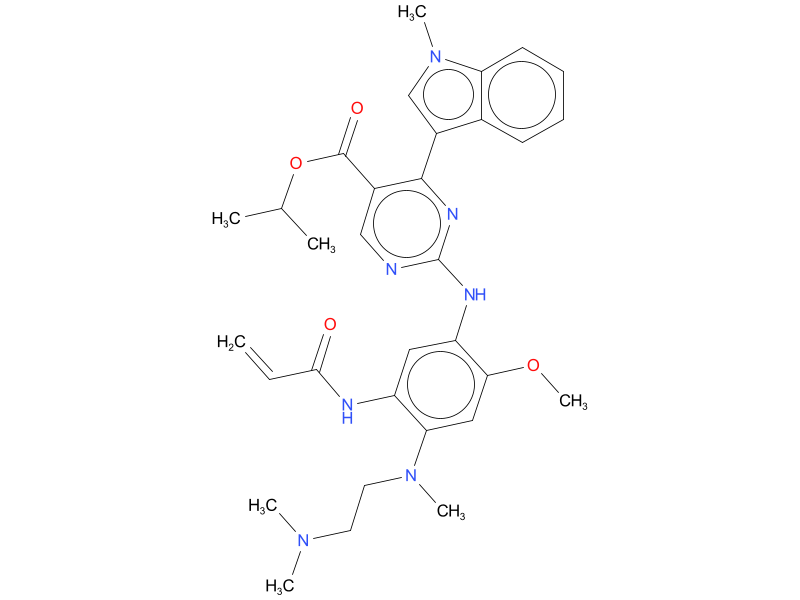
| Drug Profile | Mobocertinib is a kinase inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that irreversibly binds to and inhibits EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations at lower concentrations than wild type (WT) EGFR. Two pharmacologically-active metabolites (AP32960 and AP32914) with similar inhibitory profiles to mobocertinib have been identified in the plasma after oral administration of mobocertinib. In vitro, mobocertinib also inhibited the activity of other EGFR family members (HER2 and HER4) and one additional kinase (BLK) at clinically relevant concentrations (IC50 values <2 nM). |
| Alternative Names | AP 32788; EXKIVITY; Mobocertinib succinate – Takeda; TAK 788 |
| Originator | ARIAD Pharmaceuticals |
| Developer | ARIAD Pharmaceuticals; Takeda |
| Class | Amides; Antineoplastics; Dimethylamines; Esters; Ethers; Indoles; Pyrimidines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | BLK protein inhibitors; Epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists; ERBB 2 receptor antagonists; ERBB 4 receptor antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are two patents protecting this compound. Mobocertinib succinate has fifty-six patent family members in thirty-seven countries. |
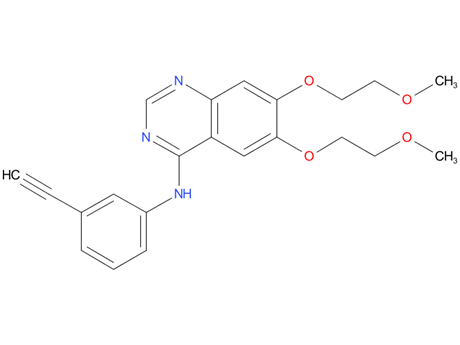
7, Lazertinib
Lazertinib is an oral, third-generation, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) being developed by Yuhan and Janssen Biotech for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It is a brain-penetrant, irreversible EGFR-TKI that targets the T790M mutation and activating EGFR mutations Ex19del and L858R, while sparing wild type-EGFR. In January 2021, lazertinib received its first approval for the treatment of patients with EGFR T790M mutation-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who have previously received EGFR-TKI therapy. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of lazertinib leading to this first approval.
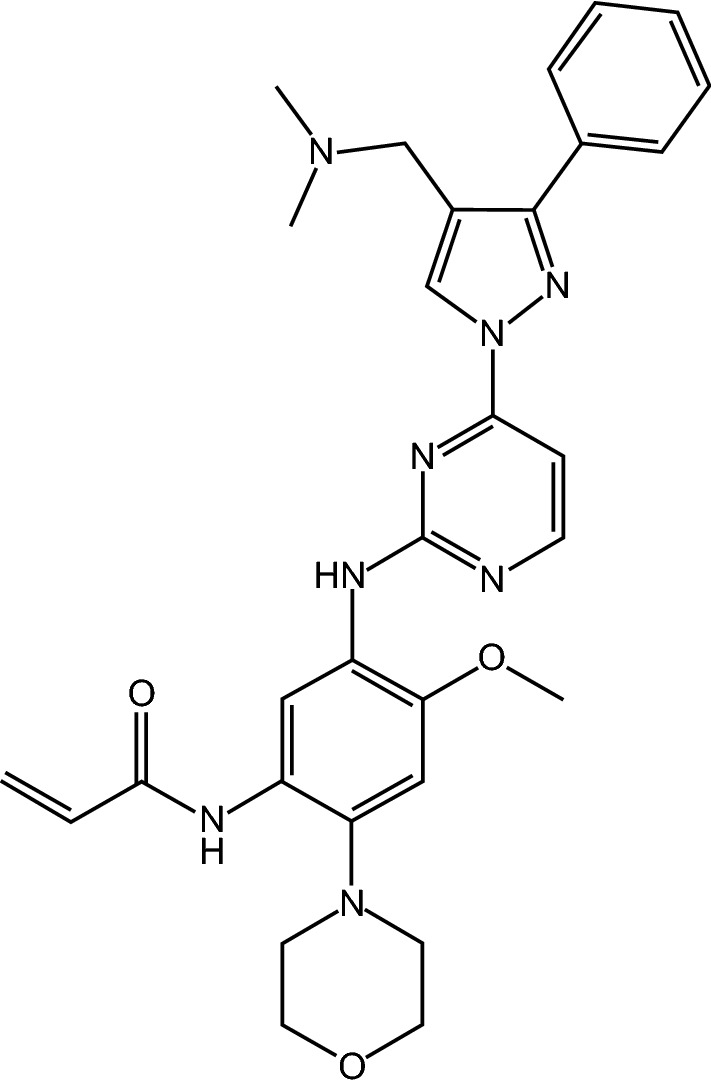
| Drug Profile | Icotinib is a new epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that developed and used in China for the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). |
| Alternative Names | BPI-2009; BPI-2009C; BPI-2009H; Conmana; Icotinib hydrochloride |
| Originator | Beta Pharma |
| Developer | Beta Pharma; Betta Pharmaceuticals Co Ltd; Zhejiang Betta Pharma |
| Class | 3-ring heterocyclic compounds; Alkynes; Antineoplastics; Crown ethers; Quinazolines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Null |
| Patent Information | Null |
Contact us to help you access the Lao pharmaceutical industry
RxLibra started its entrepreneurial journey with the vision of advancing the Lao pharmaceutical industry and becoming a global company. RxLibra is the first company in Laos to focus on exporting life-saving cancer drugs to Asia, Africa and Latin America.
Click & Contact us ?
The WTO’s Council for Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) :Under this license, the Lao pharmaceutical industry, as well as the pharmaceutical industry in similar countries(Bangladesh, Nepal, etc.), will be able to manufacture many drugs without patent authorization.
Reference:
《WTO members agree to extend drug patent exemption for poorest members》https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/news15_e/trip_06nov15_e.htm
《Product Patent Protection,the TRIPS LDC Exemption and the Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Industry》https://www.twn.my/title2/IPR/pdf/ipr17.pdf