4 kinds of targeted therapies for the treatment of Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
About Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL)
An indolent (slow-growing) cancer in which immature lymphocytes (white blood cells) are found in the blood and bone marrow and/or in the lymph nodes. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) are the same disease, but in CLL cancer cells are found mostly in the blood and bone marrow. In SLL cancer cells are found mostly in the lymph nodes. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Also called CLL/SLL.
4 kinds of targeted drugs for the treatment of Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma can be made in Laos
- Ibrutinib
- Zanubrutinib
- Idelalisib
- Duvelisib
Targeted therapy
Some oral targeted therapies are used as monotherapies — used alone to treat CLL/SLL — while in other cases they may be combined with chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or other types of treatment to be most effective.
Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors
Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) inhibitors are an evolving group of new drugs that inhibit the enzyme BTK. They help to trigger cell death by blocking the B-cell receptor signaling that leukemias and lymphomas use to grow and survive. SLL/ CLL use B-cell receptor signaling for growth and survival so blocking this pathway stops the blood cancer growing and surviving.
1、Ibrutinib
A drug used alone or with other drugs to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, small lymphocytic lymphoma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma), mantle cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma. It is also used to treat adults and children aged 1 year and older with chronic graft versus host disease. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Ibrutinib blocks a protein called BTK, which may help keep cancer cells from growing. It may also lower the body’s immune response.
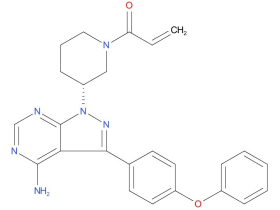
| Drug Profile | Ibrutinib is a small-molecule inhibitor of BTK. Ibrutinib forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue in the BTK active site, leading to inhibition of BTK enzymatic activity. BTK is a signaling molecule of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) and cytokine receptor pathways. BTK’s role in signaling through the B-cell surface receptors results in activation of pathways necessary for B-cell trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion. Nonclinical studies show that ibrutinib inhibits malignant B-cell proliferation and survival in vivo as well as cell migration and substrate adhesion in vitro. |
| Alternative Names | CRA-032765; IMBRUVICA; Imbruvica; ImBurvica; JNJ-54179060; PCI-32765 |
| Originator | Celera Genomics Group |
| Developer | Bristol-Myers Squibb; Celgene Corporation; Foundation GIMEMA; Genentech; Janssen; Janssen Biotech; Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation; National Cancer Institute (USA); Northwestern University; OHSU Knight Cancer Institute; Pharmacyclics; Sheba Medical Center; Singapore General Hospital; Stanford University Medical Center; Thomas Jefferson University; University Hospital Muenster; University of California, Davis; University of California, San Diego |
| Class | 2 ring heterocyclic compounds; Antiallergics; Antineoplastics; Antirheumatics; Phenyl ethers; Piperidines; Pyrazoles; Pyrimidines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Agammaglobulinaemia tyrosine kinase inhibitors; Emt protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; Mantle-cell lymphoma; Graft-versus-host disease |
| Patent Information | There are forty patents protecting this compound and three Paragraph IV challenges.Ibrutinib has three hundred and thirty-four patent family members in forty-three countries. |
2、Zanubrutinib
Zanubrutinib is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with:
- Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
- Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior treatment for their cancer.
- Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) when the disease has come back or did not respond to treatment and who have received at least one certain type of treatment.
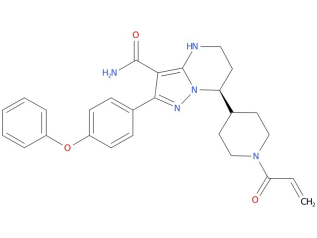
| Drug Profile | zanubrutinib is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor. Zanubrutinib forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue in the BTK active site, leading to inhibition of BTK activity. BTK is a signaling molecule of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) and cytokine receptor pathways. In B-cells, BTK signaling results in activation of pathways necessary for B-cell proliferation, trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion. In nonclinical studies, zanubrutinib inhibited malignant B-cell proliferation and reduced tumor growth. |
| Alternative Names | BGB-3111; BRUKINSA |
| Originator | BeiGene |
| Developer | BeiGene; Medison Pharma |
| Class | Amides; Antineoplastics; Phenyl ethers; Piperidines; Pyrazoles; Pyrimidines; Small molecules; Urologics |
| Mechanism of Action | Agammaglobulinaemia tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinaemia; Mantle-cell lymphoma; Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia |
| Patent Information | There are four patents protecting this compound. Zanubrutinib has forty-six patent family members in twenty-six countries. |
PI3K inhibitors
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors (PI3K inhibitors) are a class of medical drugs that are mainly used to treat advanced cancers. They function by inhibiting one or more of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) enzymes, which are part of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. This signal pathway regulates cellular functions such as growth and survival. It is strictly regulated in healthy cells, but is always active in many cancer cells, allowing the cancer cells to better survive and multiply. PI3K inhibitors block the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and thus slow down cancer growth. They are examples of a targeted therapy.
3、Idelalisib
Idelalisib is a second-line drug for patients whose chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has relapsed. Used in combination with rituximab, idelalisib is to be used in patients for whom rituximab alone would be considered appropriate therapy due to other existing medical conditions. It appears to be effective and leads to improvement of lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly.
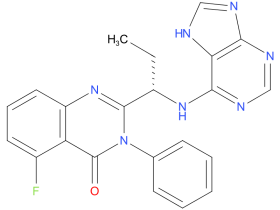
| Drug Profile | Idelalisib is an inhibitor of PI3K-delta kinase, which is expressed in normal and malignant B-cells. Idelalisib induced apoptosis and inhibited proliferation in cell lines derived from malignant B-cells and in primary tumor cells. Idelalisib inhibits several cell signaling pathways, including B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling and the CXCR4 and CXCR5 signaling, which are involved in trafficking and homing of B-cells to the lymph nodes and bone marrow. |
| Alternative Names | CAL-101; GS-1101; IDELA; Zydelig |
| Originator | Calistoga Pharmaceuticals |
| Developer | Augusta University; Calistoga Pharmaceuticals; Celgene Corporation; Gilead Sciences; Merck Sharp & Dohme; National Cancer Institute (USA) |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Purines; Quinazolinones; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase delta inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Null |
| Patent Information | There are eight patents protecting this compound. This drug has one hundred and thirteen patent family members in forty countries. |
4、Duvelisib
Duvelisib is indicated to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who have received at least two prior therapies that did not work or stopped working. CLL is a type of cancer that begins in the white blood cells, and SLL is a type of cancer that begins mostly in the lymph nodes.
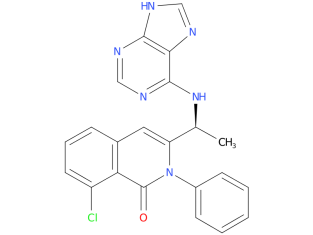
| Drug Profile | Duvelisib is an inhibitor of PI3K with inhibitory activity predominantly against PI3K-delta and PI3K-gamma isoforms expressed in normal and malignant B-cells. Duvelisib induced growth inhibition and reduced viability in cell lines derived from malignant B-cells and in primary CLL tumor cells. Duvelisib inhibits several key cell-signaling pathways, including B-cell receptor signaling and CXCR12-mediated chemotaxis of malignant B-cells. Additionally, duvelisib inhibits CXCL12-induced T cell migration and M-CSF and IL-4 driven M2 polarization of macrophages. |
| Alternative Names | ABBV-954; COPIKTRA; INK-1197; IPI-145; VS-0145; YHI-1702 |
| Originator | Intellikine |
| Developer | AbbVie; CSPC Pharmaceutical Group; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Infinity Pharmaceuticals; Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center; Secura Bio; Verastem Oncology; Yakult Honsha |
| Class | Anti-inflammatories; Antiasthmatics; Antineoplastics; Antirheumatics; Isoquinolines; Purines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase delta inhibitors; Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase gamma inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – T-cell lymphoma; Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; Peripheral T-cell lymphoma; Follicular lymphoma |
| Patent Information | There are five patents protecting this compound. This drug has one hundred and forty-seven patent family members in thirty-four countries. |
Contact us to help you access the Lao pharmaceutical industry
RxLibra started its entrepreneurial journey with the vision of advancing the Lao pharmaceutical industry and becoming a global company. RxLibra is the first company in Laos to focus on exporting life-saving cancer drugs to Asia, Africa and Latin America.
Click & Contact us?
The WTO’s Council for Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) :Under this license, the Lao pharmaceutical industry, as well as the pharmaceutical industry in similar countries(Bangladesh, Nepal, etc.), will be able to manufacture many drugs without patent authorization.
Reference:
《WTO members agree to extend drug patent exemption for poorest members》https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/news15_e/trip_06nov15_e.htm
《Product Patent Protection,the TRIPS LDC Exemption and the Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Industry》https://www.twn.my/title2/IPR/pdf/ipr17.pdf