4 kinds of targeted therapies for the treatment of RET fusion-positive non small cell lung cancer
About Non Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC)
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively (adjuvant chemotherapy).
4 kinds of targeted drugs for the treatment of About RET fusion-positive non small cell lung cancer can be made in Laos
- Selpercatinib
- Pralsetinib
- Cabozantinib
- Vandetanib
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells. Targeted therapies usually cause less harm to normal cells than chemotherapy or radiation therapy do. Monoclonal antibodies, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors are three types of targeted therapy being used to treat advanced, metastatic, or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer.
RET Inhibitors:
RET inhibitors are targeted therapies that act on tumors with activating alterations in the RET proto-oncogene, such as point mutations or fusions. They fall under the category of the tyrosine kinase inhibitors, which work by inhibiting proteins involved in the abnormal growth of cancer cells.
1, Selpercatinib
A drug used to treat certain types of non-small cell lung cancer in adults and certain types of thyroid cancer in adults and children aged 12 years and older caused by an abnormal RET gene. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Selpercatinib blocks certain proteins, including those made by the RET fusion gene or the mutated RET gene. Blocking these proteins may help keep cancer cells from growing.
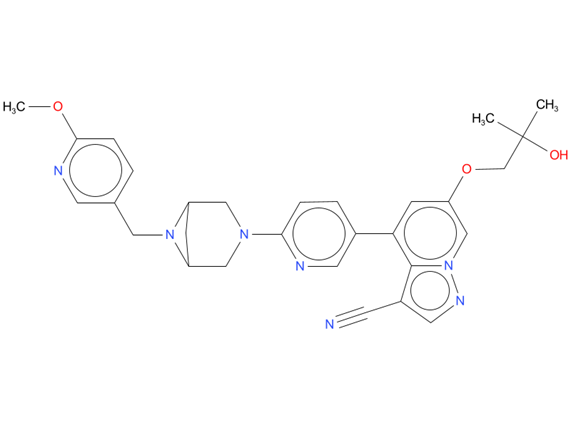
| Drug Profile | Selpercatinib is a kinase inhibitor. Selpercatinib inhibited wild-type RET and multiple mutated RET isoforms as well as VEGFR1 and VEGFR3 with IC50 values ranging from 0.92 nM to 67.8 nM. In other enzyme assays, selpercatinib also inhibited FGFR 1, 2, and 3 at higher concentrations that were still clinically achievable. In cellular assays, selpercatinib inhibited RET at approximately 60-fold lower concentrations than FGFR1 and 2 and approximately 8-fold lower concentration than VEGFR3 |
| Alternative Names | LOXO 292; LY-3527723; RETEVMOTM; Retsevmo |
| Originator | Array BioPharma |
| Developer | Eli Lilly and Company; Loxo Oncology |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Aza compounds; Ethers; Nitriles; Pyrazoles; Pyridines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Proto oncogene protein c ret inhibitors; Type 1 fibroblast growth factor receptor antagonists; Type 3 fibroblast growth factor receptor antagonists; Type-2 fibroblast growth factor receptor antagonists; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 antagonists; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Thyroid cancer; Pancreatic cancer; Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are five patents protecting this compound. Selpercatinib has seventy-six patent family members in thirty-six countries. |
2, Pralsetinib
Pralsetinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with metastatic RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) as detected by an FDA approved test.
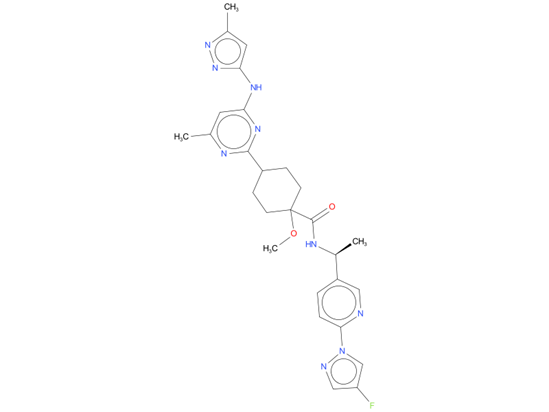
| Drug Profile | Pralsetinib is a kinase inhibitor of wild-type RET and oncogenic RET fusions (CCDC6-RET) and mutations (RET V804L, RET V804M and RET M918T) with half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) less than 0.5 nM. In purified enzyme assays, pralsetinib inhibited DDR1, TRKC, FLT3, JAK1-2, TRKA, VEGFR2, PDGFRb, and FGFR1 at higher concentrations that were still clinically achievable at Cmax. In cellular assays, pralsetinib inhibited RET at approximately 14-, 40-, and 12-fold lower concentrations than VEGFR2, FGFR2, and JAK2, respectively. |
| Alternative Names | BLU-667; CS 3009; Gavreto; Pratinib; RG 6396 |
| Originator | Blueprint Medicines |
| Developer | Blueprint Medicines; CStone Pharmaceuticals; Roche |
| Class | Amides; Amines; Antineoplastics; Cyclohexanes; Ethers; Fluorinated hydrocarbons; Pyrazoles; Pyridines; Pyrimidines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Proto oncogene protein c ret inhibitors |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Thyroid cancer; Non-small cell lung cancer |
| Patent Information | There are two patents protecting this compound. Pralsetinib has forty-seven patent family members in twenty-four countries. |
3, Cabozantinib
Cabozantinib is used in two forms. A capsule form (Cometriq) is used since 2012, to treat medullary thyroid cancer and a tablet form (Cabometyx) is used since 2016, as a second line treatment for renal cell carcinoma.
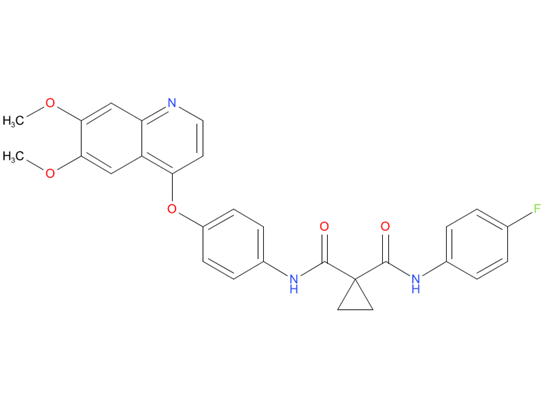
| Drug Profile | Cabozantinib inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity of MET, VEGFR-1, -2 and -3, AXL, RET, ROS1, TYRO3, MER, KIT, TRKB, FLT-3, and TIE-2. These receptor tyrosine kinases are involved in both normal cellular function and pathologic processes such as oncogenesis, metastasis, tumor angiogenesis, drug resistance, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment. |
| Alternative Names | BMS-907351; CABOMETYX; Cabometyx; Cabozantinib s-malate; Cometriq; XL-184 |
| Originator | Exelixis |
| Developer | Bristol-Myers Squibb; Centre Francois Baclesse; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Duke University Medical Center; Emory University; Exelixis; Ipsen; Massachusetts General Hospital; Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center; Merck Sharp & Dohme; National Cancer Institute (USA); Roche; Swedish Orphan Biovitrum; Takeda; University of California at Irvine; University of Kentucky |
| Class | Amides; Anilides; Antineoplastics; Cyclopropanes; Fluorine compounds; Quinolines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Axl receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors; Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors; Proto oncogene protein c met inhibitors; Proto oncogene protein c ret inhibitors; TIE 2 receptor antagonists; TrkB receptor antagonists; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 antagonists; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 antagonists; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Thyroid cancer; Liver cancer |
| Patent Information | There are twelve patents protecting this compound. Cabozantinib s-malate has two hundred and thirty patent family members in thirty-four countries. |
4, Vandetanib
A drug used to treat medullary thyroid cancer that is locally advanced and cannot be removed by surgery or has spread to other parts of the body. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer. Vandetanib blocks certain proteins, which may help keep cancer cells from growing. It may also prevent the growth of new blood vessels that tumors need to grow.
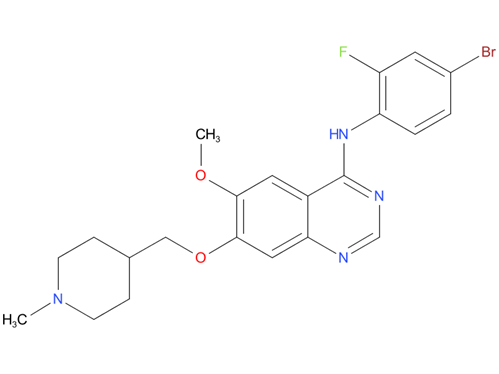
| Drug Profile | In vitro studies have shown that vandetanib inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity of the EGFR and VEGFR families, RET, BRK, TIE2, and members of the EPH receptor and Src kinase families. These receptor tyrosine kinases are involved in both normal cellular function and pathologic processes such as oncogenesis, metastasis, tumor angiogenesis, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment. In addition, the N-desmethyl metabolite of the drug, representing 7 to 17.1% of vandetanib exposure, has similar inhibitory activity to the parent compound for VEGF receptors (KDR and Flt-1) and EGFR. In vitro, vandetanib inhibited epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in tumor cells and endothelial cells and VEGF-stimulated tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in endothelial cells. In vivo, vandetanib administration reduced tumor cell-induced angiogenesis, tumor vessel permeability, and inhibited tumor growth and metastasis in mouse models of cancer. |
| Alternative Names | AZD 6474; Caprelsa; SAR 390530; Zactima; ZD 6474; Zictifa |
| Originator | AstraZeneca |
| Developer | AstraZeneca; Fox Chase Cancer Center; Hoosier Cancer Research Network; Sanofi; University of Oxford |
| Class | Antineoplastics; Bromobenzenes; Fluorobenzenes; Piperidines; Quinazolines; Small molecules |
| Mechanism of Action | Epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists; Proto oncogene protein c ret inhibitors; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 antagonists |
| Orphan Drug Status | Yes – Thyroid cancer |
| Patent Information | There are three patents protecting this compound. Vandetanib has one hundred and forty-two patent family members in forty-three countries. |
Contact us to help you access the Lao pharmaceutical industry
RxLibra started its entrepreneurial journey with the vision of advancing the Lao pharmaceutical industry and becoming a global company. RxLibra is the first company in Laos to focus on exporting life-saving cancer drugs to Asia, Africa and Latin America.
Click & Contact us ?
The WTO’s Council for Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) :Under this license, the Lao pharmaceutical industry, as well as the pharmaceutical industry in similar countries(Bangladesh, Nepal, etc.), will be able to manufacture many drugs without patent authorization.
Reference:
《WTO members agree to extend drug patent exemption for poorest members》https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/news15_e/trip_06nov15_e.htm
《Product Patent Protection, the TRIPS LDC Exemption and the Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Industry》https://www.twn.my/title2/IPR/pdf/ipr17.pdf